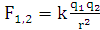|
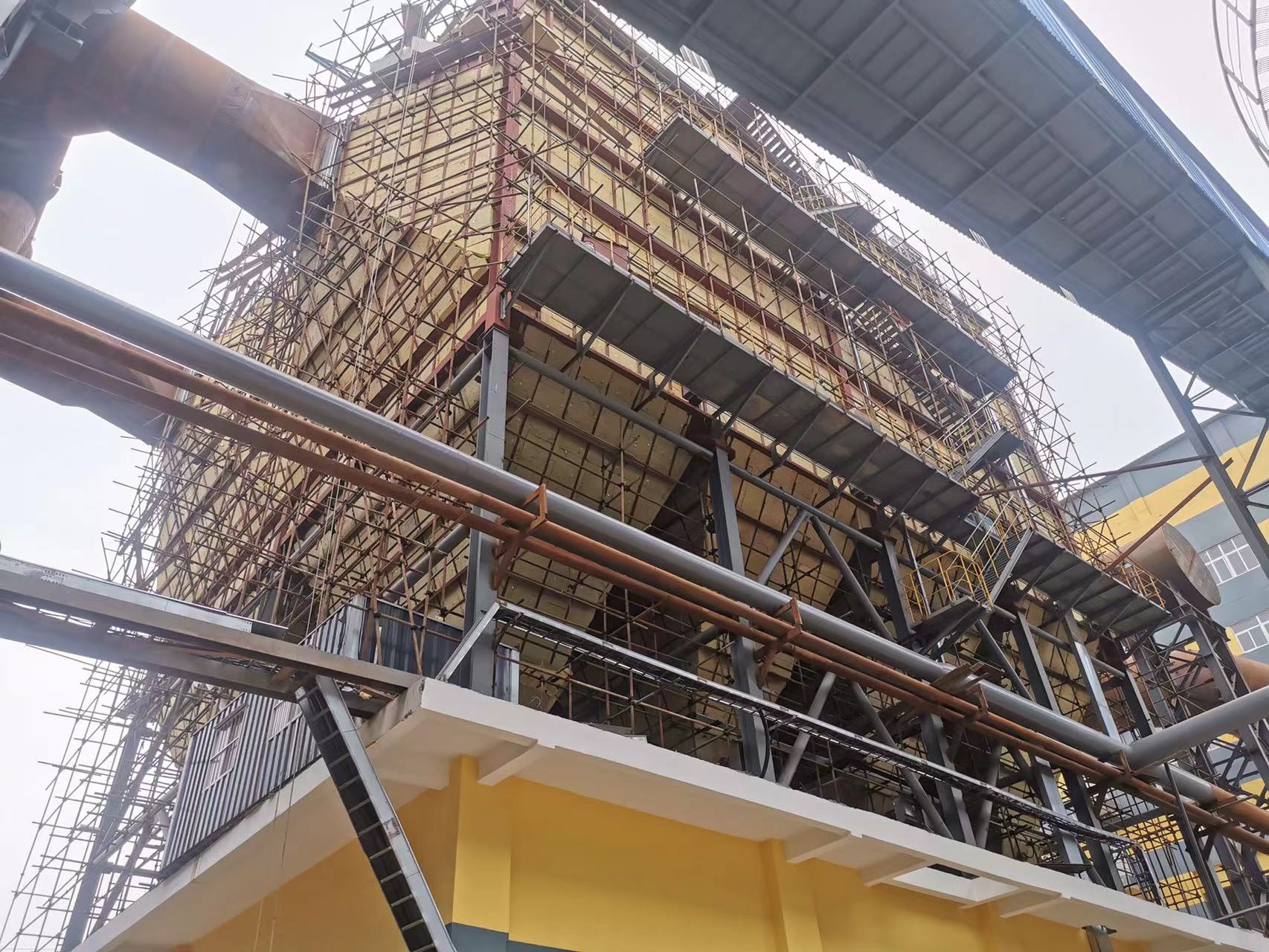
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
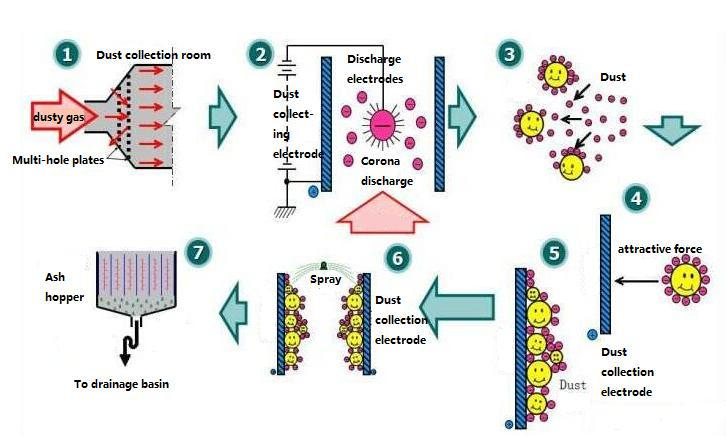
Basic principles of the Coulomb electric field i.e. Basic principles of electrostatic precipitators The separation of suspended dust particles in a gas by means of electric dedusting consists of four complex and interrelated physical processes, as follows. 1.Ionisation of gases. 2.Charging of suspended dust particles. 3.Movement of charged dust particles towards the electrodes. (embodied by Coulomb forces) 4.Charged dust particles are deposited on the electrodes.
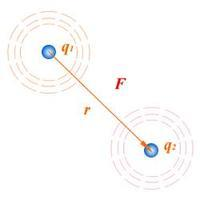
Principle of the Coulomb Electrostatic Precipitator Electrostatic precipitation technology is derived from Coulomb's Law, the basic theory of electrostatics, F: Coulombic force, i.e. the attractive force between the charged dust particles and the dust accumulation pole of the anode plate. r: distance between the charged dust particle and the dust accumulation pole of the anode plate. k: electrostatic force constant. q1, q2: amount of dust charge, amount of dust accumulation pole (anode plate) charge.
The magnitude of the Coulom bforce is inversely proportional to the square of the distance rbetween the two point charges,and is proportional to the product of the charge amounts. 1.Process flow of conventional ESP
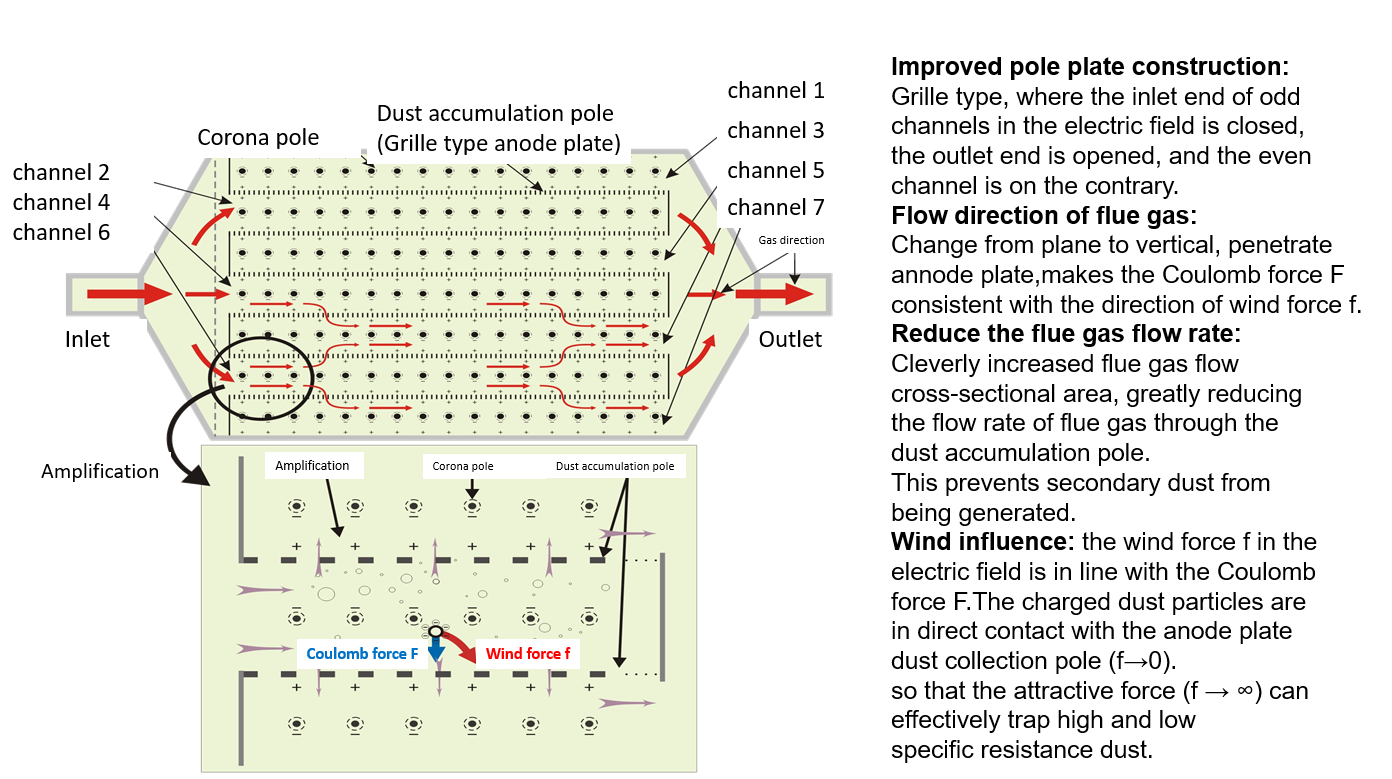
1.Process flow of the Coulomb ESP
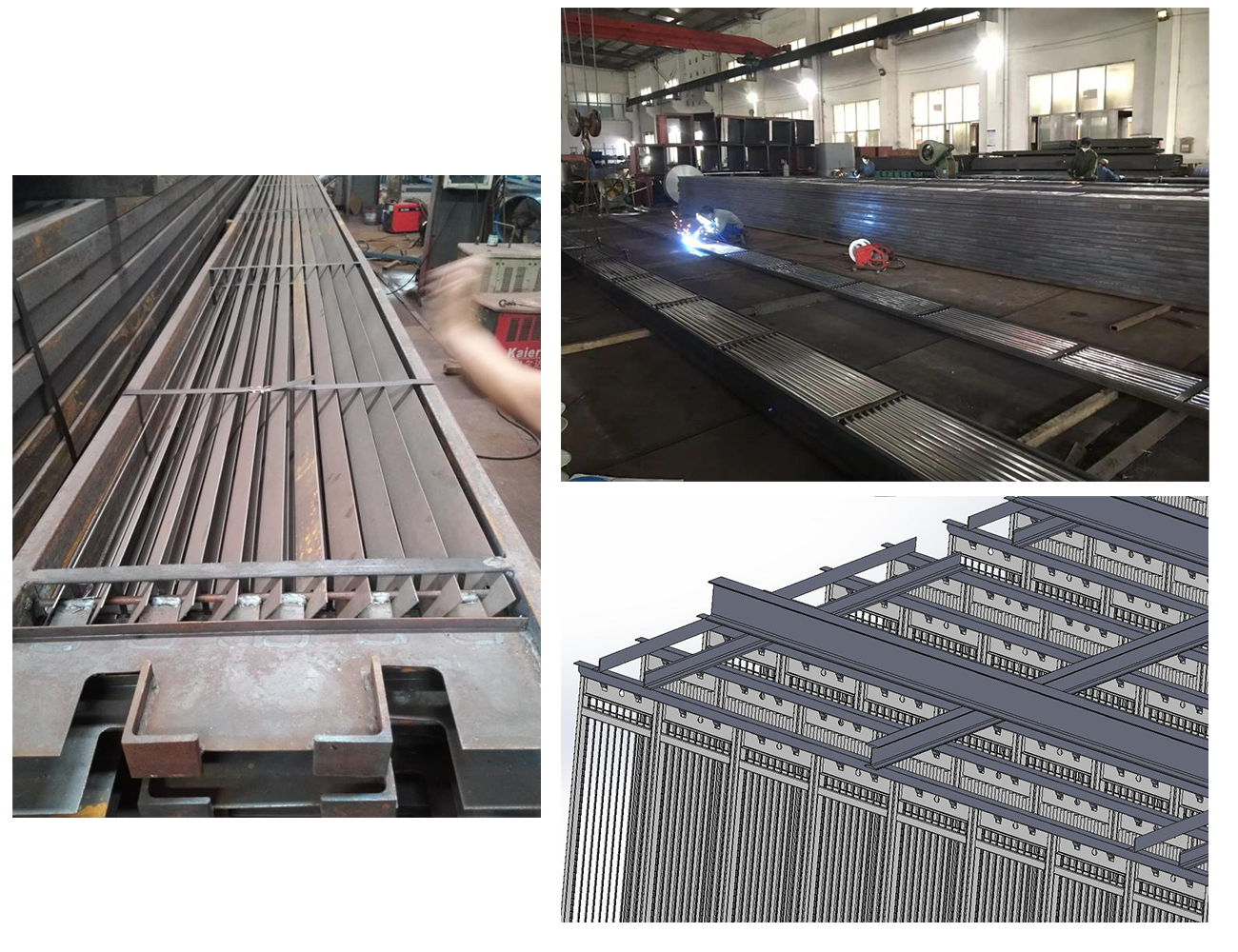
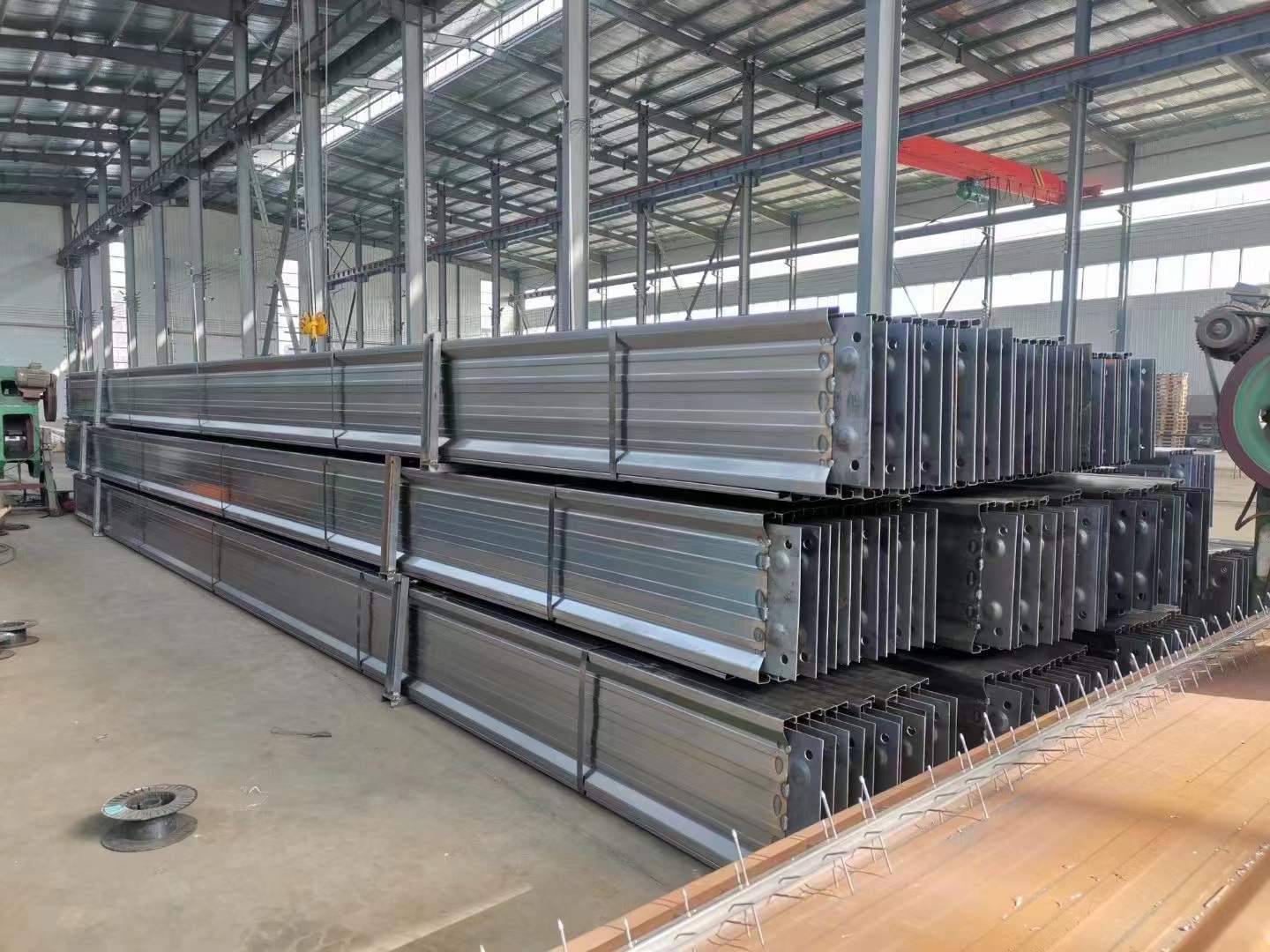
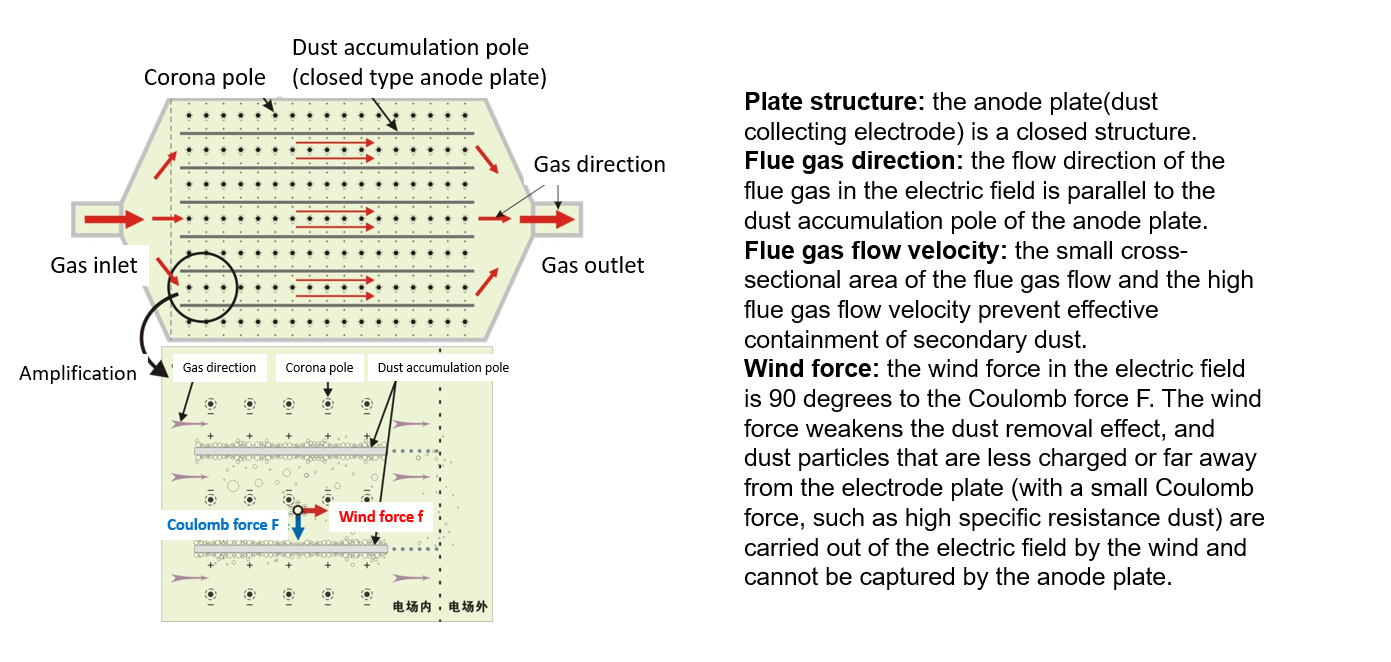
Illustration of Coulomb anode plate
|